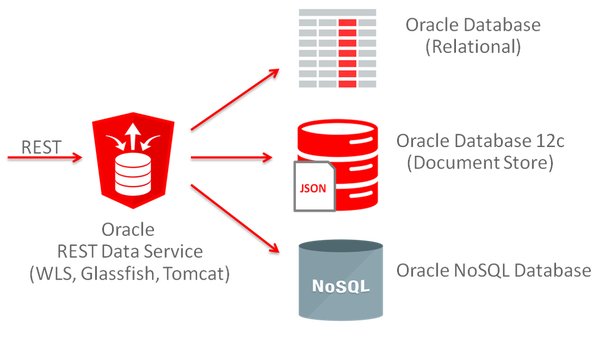
ORDS allows you to capture or expose data in an Oracle Database (relational or NoSQL) using the ubiquitous REST protocol. It runs as a Java application and works with APEX, offering features like OAuth2 authentication and automatic JSON parsing.

What is ORDS?
Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) is a Java-based application that enables you to expose Oracle Database data and functionality through RESTful web services. It provides:
- RESTful access to Oracle Database
- Support for JSON and other formats
- OAuth2 authentication
- Integration with Oracle APEX
- Automatic JSON parsing and generation
Use Cases
ORDS is versatile and can be used in many scenarios:
Exposing Oracle e-Business Suite Data
Create REST APIs that expose EBS data to external systems, mobile applications, or other integration points without modifying core EBS code.
IoT Data Capture
Use ORDS with Oracle NoSQL databases to capture high-volume IoT sensor data through simple REST endpoints.
Custom Integration Middleware
Build lightweight integration solutions using ORDS as the communication layer between systems.
Point-to-Point Integrations
For small and medium businesses, ORDS provides a cost-effective alternative to enterprise service bus solutions for simple integrations.
Understanding REST Principles
Before implementing ORDS, it’s important to understand REST fundamentals. I recommend the APIGEE paper “Web API Design - Crafting Interfaces that Developers Love” by Brian Mulloy.
Key REST principles to follow:
- Use nouns, not verbs, in URLs
- Use HTTP methods appropriately (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Return meaningful HTTP status codes
- Version your APIs
- Provide clear documentation
Best Practices
URL Design and Schema Naming
Your URL structure should be intuitive and consistent:
https://server/ords/schema/module/resourceConsider using a dedicated schema for ORDS services rather than mixing with application schemas.
API Versioning
Use modules for versioning, allowing v1 and v2 consumers to coexist:
https://server/ords/api/v1/customers
https://server/ords/api/v2/customersDeployment via SQL Scripts
Maintain your ORDS definitions in SQL scripts for version control and repeatable deployments:
BEGIN
ORDS.DEFINE_MODULE(
p_module_name => 'v1',
p_base_path => '/v1/',
p_items_per_page => 25
);
END;
/Authentication and Authorization
Always secure your APIs appropriately:
- Use OAuth2 for external consumers
- Implement role-based access control
- Never expose sensitive data without authentication
Clear Error Messaging
Provide meaningful error messages that help developers understand and resolve issues:
{
"error": "Invalid customer ID",
"detail": "Customer ID must be a positive integer",
"status": 400
}Conclusion
ORDS is a powerful tool for exposing Oracle Database data through REST APIs. By following REST principles and ORDS best practices, you can build robust, scalable, and maintainable integration solutions.
Jon Dixon, Co-Founder JMJ Cloud