This post provides a comprehensive guide to implementing OAuth2 client credentials (two-legged OAuth) security for Oracle REST Data Services.
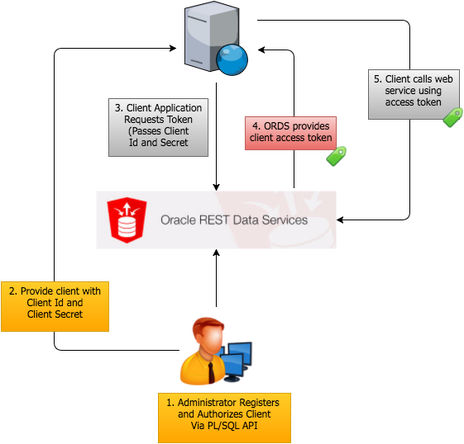
Overview of OAuth2 Approaches
ORDS supports two OAuth2 models:
Two-legged OAuth involves a calling application and API provider, typically for server-to-server interactions where the calling system can securely store credentials.
Three-legged OAuth adds an end-user authorization layer for consumer-facing scenarios where user consent is required.
This post focuses on the two-legged client credentials flow.
Client Credentials Flow Steps
The implementation involves five key steps:
- Develop and secure a REST service with a privilege
- Register a client application
- Store credentials securely in the calling system
- Exchange credentials for an access token
- Call the service with the bearer token
Step 1: Create a Privilege
Use ords.create_privilege() to define a privilege that will protect your REST service:
BEGIN
ORDS.CREATE_PRIVILEGE(
p_name => 'example_priv',
p_role_name => 'example_role',
p_description => 'Privilege for example REST service'
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
Step 2: Map the Privilege to Services
Use ords.create_privilege_mapping() to associate the privilege with your REST endpoints:
BEGIN
ORDS.CREATE_PRIVILEGE_MAPPING(
p_privilege_name => 'example_priv',
p_pattern => '/example/*'
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
Step 3: Register a Client Application
Register the calling application using oauth.create_client():
BEGIN
OAUTH.CREATE_CLIENT(
p_name => 'Example Client',
p_grant_type => 'client_credentials',
p_owner => 'Example Corp',
p_description => 'Client for example integration',
p_support_email => '[email protected]',
p_privilege_names => 'example_priv'
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
After registration, retrieve the client ID and secret:
SELECT id, name, client_id, client_secret
FROM user_ords_clients
WHERE name = 'Example Client';Step 4: Obtain Authorization Token
Exchange credentials for an access token via POST to the ORDS token endpoint:
curl -X POST \
https://your-server/ords/schema/oauth/token \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "grant_type=client_credentials" \
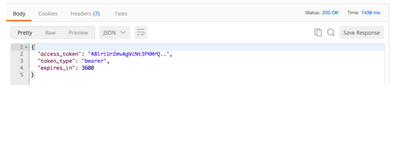
-u "client_id:client_secret"The response includes the access token:
{
"access_token": "abc123xyz...",
"token_type": "bearer",
"expires_in": 3600
}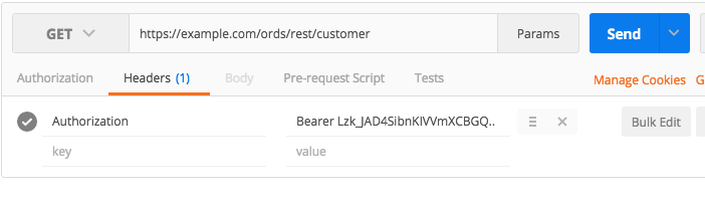
Step 5: Call the Secured Service
Include the token in the Authorization header when calling secured services:
curl -X GET \
https://your-server/ords/schema/example/resource \
-H "Authorization: Bearer abc123xyz..."Token Management
Tokens expire after 3,600 seconds (1 hour) by default. When services return HTTP 401 status, clients must request fresh tokens.
Best practices:
- Cache tokens until they expire
- Implement automatic token refresh on 401 responses
- Store credentials securely (never in source code)
- Use HTTPS for all token exchanges
Conclusion
OAuth2 client credentials flow provides secure server-to-server authentication for ORDS REST services. The five-step process - create privilege, map to services, register client, obtain token, call service - provides a robust security model for integration scenarios.
Jon Dixon, Co-Founder JMJ Cloud