APEX was born for the Cloud given its web-based development environment and natural container in the Oracle Database. This post explores four primary use cases for Oracle APEX as a Platform-as-a-Service solution for Cloud ERP integration.
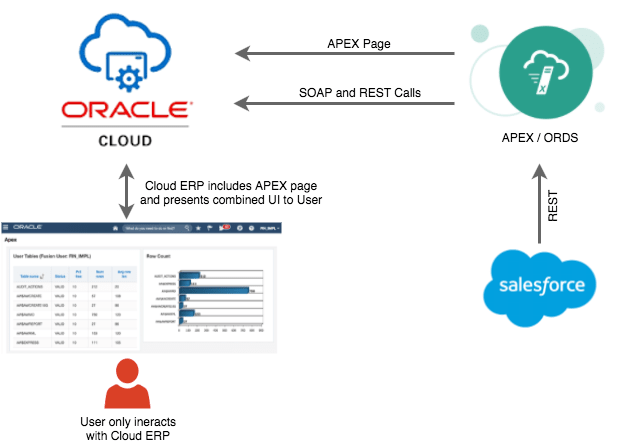
Use Case 1: Cloud ERP/APEX UI Mashup
Embed APEX pages directly within the Cloud ERP interface. Users navigate to integrated pages from within ERP, and the APEX content displays seamlessly.
Example: An embedded APEX page enables ERP users to search Salesforce prospects in real-time and convert them to ERP customers using JWT authentication for secure single sign-on.
This approach provides:
- Seamless user experience
- Real-time external data access
- Custom functionality beyond standard ERP
Use Case 2: Standalone Cloud ERP Connected Apps

Build standalone APEX applications that consume Cloud ERP data and combine it with other sources.
Example: A consolidated financial dashboard that:
- Pulls data from Cloud ERP via BI Publisher web services
- Combines with treasury system data
- Integrates SAP subsidiary information
- Uses ERP credentials for authentication
- Caches data locally to reduce latency
Benefits include:
- Consolidated view across systems
- Custom reporting beyond ERP capabilities
- Reduced ERP load through local caching
Use Case 3: Standalone Mobile APEX Apps
APEX’s responsive design enables rapid development of mobile applications that interact with Cloud ERP.
Example: Project managers capture worksite images using mobile devices and upload them as attachments to ERP projects via REST APIs.
Mobile use cases include:
- Field data capture
- Approval workflows
- Status updates
- Document attachments
- Time and expense entry
Use Case 4: Integration Platform
Use APEX with ORDS as a lightweight integration solution between Cloud ERP and other systems.
Example: Scheduled database jobs that:
- Synchronize employees between Workday and Cloud ERP
- Run on configurable schedules
- Log all transactions
- Send automated email alerts on failures
- Provide dashboard visibility into sync status
This positions APEX/ORDS as a cost-effective alternative to enterprise SOA solutions for simpler integration needs.
Key Considerations
Security
You need to be extra careful with security when building PaaS extensions. Consider:
- JWT token validation
- OAuth2 authentication
- Network security and firewalls
- Data encryption in transit
REST vs SOAP
Prefer REST services over SOAP where possible. Cloud ERP provides comprehensive REST APIs that are easier to consume from APEX.
Licensing
Consult with Oracle regarding licensing implications for your specific use case. Cloud services and database editions have different licensing terms.
Cost-Effectiveness
APEX provides significant cost savings compared to:
- Custom Java development
- Enterprise service bus solutions
- Third-party integration platforms
Hosting Options
APEX can run on:
- Exadata Express ($175/month for 20GB)
- Oracle Database Cloud Service
- Autonomous Database
- On-premise Oracle Database
Conclusion
APEX is an underrated option for Cloud ERP integration scenarios. Its combination of:
- Rapid development capabilities
- Low infrastructure requirements
- No additional licensing (with Oracle Database)
- Strong REST API support
- Responsive design for mobile
Makes it an excellent choice for extending Cloud ERP functionality through PaaS.
Jon Dixon, Co-Founder JMJ Cloud